“Free float” refers to the portion of a company’s outstanding shares that are available for trading in the stock market. It is calculated by subtracting the number of restricted shares, such as those held by company insiders or subject to lock-up agreements, from the total number of outstanding shares. The term free float is sometimes referred to as the public float of a company.
Free float is an important consideration for index providers, such as MSCI, because it reflects the portion of a company’s stock that is accessible to the general public. In determining the composition of its indices, MSCI typically uses a free float-adjusted market capitalization weighting, which means that companies with a higher free float have a greater impact on the index’s performance.
This approach is meant to ensure that the indices accurately reflect the investment opportunity set available to the general public, as it is more representative of the market capitalization that is actually available for investment. For example, a company with a high level of insider ownership or restricted shares may have a large market capitalization, but the free float may be much smaller and therefore have a limited impact on the index.
In summary, free float is a crucial consideration for investors and index providers, as it provides a more accurate representation of a company’s market capitalization and the investment opportunity set available to the public.
How to check the free-float market capitalization of a listed Indian company?
The free-float market capitalization of a listed Indian company can be checked on the official stock exchange website, nseindia or bseindia.
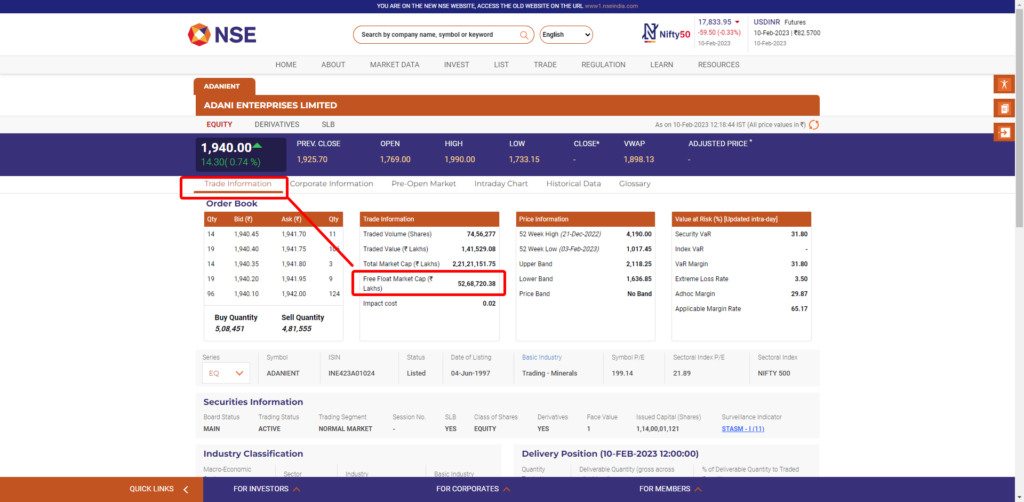

To find the free float as a percentage of the Total Market Capitalization of that company, use the formula, ( Free Float Market Capitalization / Full Market Capitalization ) * 100.