Interest rate derivatives are financial contracts that allow investors to manage their exposure to changes in interest rates. These instruments derive their value from the movement of interest rates and are used to hedge against or speculate on changes in interest rates. Interest rate derivatives are used extensively by banks, corporations, and other market participants to manage their interest rate risk.
There are several types of interest rate derivatives, including:
- Interest rate swaps: These are contracts in which two parties agree to exchange a series of cash flows based on a fixed and floating interest rate. The most common type of interest rate swap is the plain vanilla interest rate swap, which involves the exchange of fixed-rate payments for floating-rate payments.
- Interest rate futures: These are standardized contracts that allow investors to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on a future date. Interest rate futures are based on an underlying index such as the LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) or the T-bill rate.
- Interest rate options: These are contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a specific date. Interest rate options can be used to hedge against or speculate on changes in interest rates.
- Swaptions: These are options on interest rate swaps, which give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to enter into an interest rate swap at a specified price on or before a specific date.
Interest rate derivatives are complex financial instruments that can be used for a variety of purposes, including hedging, speculating, and arbitrage. They are commonly used by financial institutions and corporations to manage their exposure to changes in interest rates and to generate income from interest rate differentials.
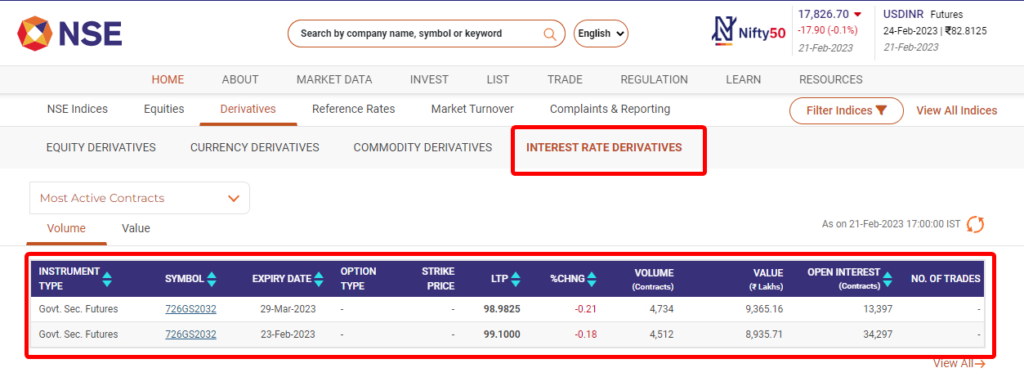
Example of interest rate derivatives traded in India.